Artificial intelligence is fundamentally transforming how individuals manage their health and wellness. Rather than waiting for symptoms to manifest, people can now harness AI-powered tools to take a proactive approach to their well-being, gaining personalized insights and guidance that were previously available only to elite athletes or wealthy individuals receiving concierge medical care. This comprehensive guide explores the practical ways AI can enhance your health journey, the underlying technologies making this possible, and important considerations for responsible adoption.
Understanding AI in Personal Health Management
Artificial intelligence in healthcare refers to computer systems designed to analyze vast amounts of health data and identify patterns that would be impossible for humans to detect manually. Unlike traditional one-size-fits-all health recommendations, AI adapts to individual circumstances by learning from personal data including fitness metrics, sleep patterns, dietary habits, genetic information, and medical history.
The transformation is significant because healthcare traditionally operated on a reactive model—individuals sought treatment after becoming ill. AI enables a shift toward predictive and preventative care, identifying health risks before they develop into serious conditions. This fundamental change in approach is reshaping how individuals think about their health management and responsibility for wellness.
Personalized Health Monitoring Through Wearable Devices
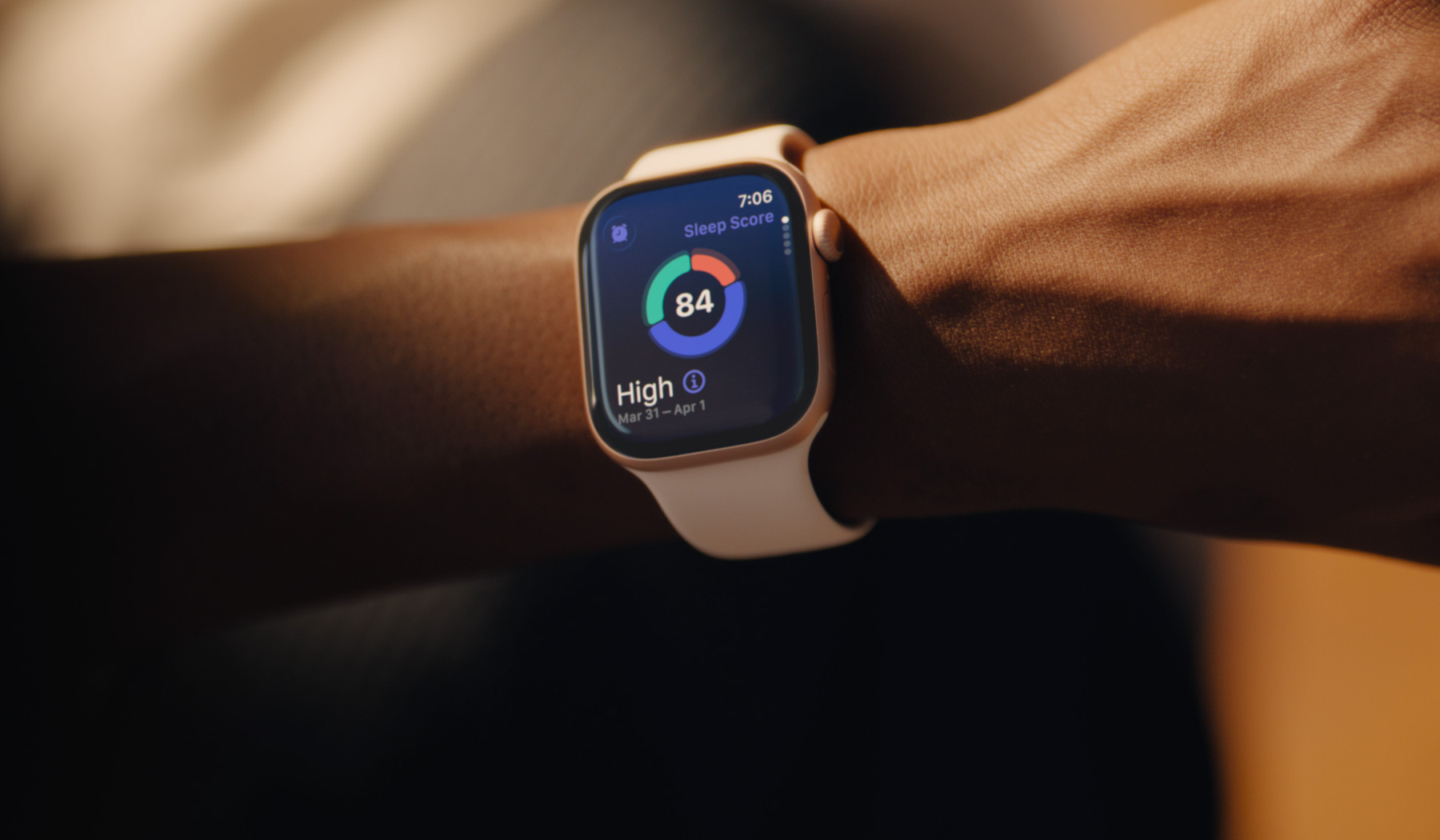
One of the most accessible applications of AI is through wearable technology and fitness trackers. Modern smartwatches and biosensors equipped with AI algorithms continuously collect biometric data—heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, sleep quality, physical activity, and even stress levels—throughout the day.
These devices transcend simple activity counting. AI-powered wearables analyze movement patterns, detect irregular heart rhythms, and identify early warning signs of health conditions before clinical symptoms appear. For instance, Apple Watch and Fitbit use AI to detect atrial fibrillation, a serious heart rhythm disorder that often goes undiagnosed until it causes complications. Some devices can identify abnormal sleep patterns indicative of sleep apnea with accuracy comparable to professional sleep studies, alerting users to seek medical evaluation.
The real power emerges from continuous monitoring over extended periods. Unlike periodic doctor visits, wearables generate longitudinal data that reveals trends and patterns unique to each individual. This data feeds into machine learning algorithms that learn your baseline health metrics and alert you when significant deviations occur.
AI-Powered Mental Health and Emotional Wellness Support
Mental health represents another frontier where AI is making significant strides. The global AI mental health market reached 1.13 billion dollars in 2023 and is projected to grow 24 percent annually through 2030, reflecting growing demand for accessible emotional support.
AI-driven mental health apps such as Wysa, Youper, and Woebot provide 24/7 emotional support through conversational AI trained on evidence-based therapeutic techniques including Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), and Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT). Unlike human therapists constrained by appointment schedules, these platforms offer immediate support whenever individuals need it, without waitlists or the cost barrier of traditional therapy.
Research demonstrates meaningful impact: a Stanford study found that 80 percent of Youper users reported improved wellbeing, with improvements often appearing within just two weeks. Early studies indicate AI chatbots can reduce depression and anxiety in just a few weeks. These apps track mood patterns over time, offering personalized guidance that adapts to each individual’s emotional trajectory and specific challenges.
The anonymity these platforms provide is particularly valuable for individuals hesitant about traditional therapy. Many people find it easier to open up to AI without fear of judgment, making these tools an effective entry point into mental health support.
Fitness and Exercise Optimization
The era of generic workout programs has ended. AI now enables truly personalized fitness through adaptive training algorithms that adjust in real-time based on your current state. Rather than following a static routine, AI fitness apps analyze your sleep quality, energy levels, heart rate variability, recovery status, and even mood to calibrate workout intensity and type.
Apps like Zing Coach check in with you daily regarding sleep, energy levels, and emotional state, then recalibrate your training plan accordingly. If you slept poorly, the AI might suggest restorative exercises instead of high-intensity training. If your heart rate variability indicates elevated stress, the algorithm might recommend flexibility work or active recovery. This dynamic approach prevents overtraining injuries while optimizing performance gains.
Real-time form correction represents another breakthrough. Computer vision algorithms analyze your movement during exercise, identifying postural flaws that could lead to injury, and provide immediate feedback to correct form. This functionality approximates having a personal trainer available for every workout.
The personalization extends to goal setting. AI algorithms learn from your progress patterns, adjusting goals to remain challenging yet achievable—preventing both discouragement from unrealistic targets and stagnation from insufficient challenge.
Nutritional Guidance and Dietary Management
Personalized nutrition represents perhaps the most complex health domain, yet AI is making substantial progress. Rather than generic dietary recommendations, AI-driven nutrition systems analyze individual factors including age, body composition, metabolism, health goals, genetic predispositions, and medical conditions to generate customized meal plans.
These systems go beyond simple calorie counting. They consider macronutrient balance, micronutrient adequacy, and alignment with established medical guidelines for specific conditions. AI nutrition platforms for diabetes and obesity management achieve approximately 80 percent adherence to health guidelines, with 72.7 percent of participants achieving diabetes remission rates in some studies. A 39 percent reduction in IBS symptom severity has been documented when individuals follow AI-generated dietary recommendations.
Some advanced systems incorporate sustainability considerations, preferring seasonal and locally sourced ingredients while meeting nutritional targets. This addresses not only individual health but also environmental impact—recognizing that true wellness encompasses planetary health.
Importantly, these systems adapt. If you consume foods that trigger negative responses, the AI learns and adjusts future recommendations. If your health markers improve with specific nutritional patterns, the algorithm refines meal suggestions accordingly.
Sleep Quality Enhancement and Sleep Disorder Detection
Sleep fundamentally impacts health, yet many individuals struggle with sleep quality without understanding underlying causes. AI-powered sleep analysis represents a breakthrough in this domain. Wearable devices and home sleep testing devices now use machine learning to analyze sleep architecture—identifying sleep stages, detecting respiratory events, and assessing sleep quality.
More remarkably, AI can diagnose sleep apnea from snoring patterns alone with 92.5 percent accuracy, potentially identifying millions of previously undiagnosed cases. The FDA has cleared several AI-powered home sleep testing devices that provide accuracy comparable to in-lab polysomnography studies—the previous gold standard—but with the convenience of home testing.
Beyond diagnosis, AI personalizes sleep improvement recommendations. The Calm and Headspace apps use AI to curate sleep stories, nature soundscapes, and meditations tailored to individual preferences, with studies showing AI-personalized sleep interventions significantly improve sleep quality compared to generic options.
Chronic Disease Management and Early Detection.
For individuals with chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, or cardiovascular disease, AI provides transformative management capabilities. Predictive analytics analyze health data to forecast disease progression, enabling earlier interventions before complications develop.
AI systems can identify patients at high risk of complications—such as hospital readmission or adverse medication interactions—allowing proactive preventative measures. Clinical decision support systems incorporating AI improve diagnostic accuracy across chronic conditions and reduce diagnostic delay.
Importantly, remote patient monitoring powered by AI enables continuous oversight of chronic conditions outside traditional clinic visits. Individuals with managed conditions can have their data analyzed automatically, with AI flagging concerning trends that warrant clinician attention. This approach has proven particularly valuable in rural and underserved areas with limited healthcare access.
The impact on disease prevention extends to infectious disease. AI has helped forecast disease outbreaks by analyzing diverse datasets, enabling targeted public health responses that mitigate disease spread before it escalates.
Practical Steps to Leverage AI for Your Health
Start with wearables: If you don’t own a health-tracking device, beginning with a smartwatch or fitness tracker provides the foundation for AI analysis. Apple Watch, Fitbit, Garmin, and Samsung Galaxy Watch all integrate sophisticated AI analysis into their ecosystems.
Choose evidence-based apps: When selecting AI health apps, prioritize those with clinical validation and published research. Apps like Wysa, Youper, Calm, and Headspace have undergone rigorous testing; verify that mental health apps cite research backing their effectiveness.
Maintain consistent data entry: AI improves with more comprehensive data. Whether tracking mood, nutrition, exercise, or symptoms, consistency enables more accurate personalization. Most apps learn from several weeks of data before producing truly personalized insights.
View AI as support, not replacement: AI should enhance—not replace—your relationship with healthcare providers. Share AI-generated insights with your doctor, particularly regarding health concerns or significant changes in health metrics.
Prioritize data security: Before adopting any health app, review its privacy policy and data security practices. Understand whether your data is encrypted, how long it’s retained, and whether it’s shared with third parties.
Important Limitations and Ethical Considerations
While AI offers tremendous promise, several important limitations warrant consideration. First, AI is not universally superior to human judgment. Early AI diagnostic systems have sometimes underperformed compared to experienced clinicians, particularly in complex cases. AI excels at pattern recognition in large datasets but may struggle with rare presentations or unusual cases.
Algorithmic bias represents a serious concern. If AI systems are trained on non-representative data, they may produce biased recommendations that perform poorly for certain populations. A widely-cited example involved healthcare allocation algorithms that systematically disadvantaged Black patients because they used historical spending patterns that reflected prior systemic biases.
Data privacy and security remain substantial concerns, particularly given that health data is highly sensitive and valuable to cybercriminals. Healthcare data breaches have exposed millions of records, compromising privacy. As AI systems require vast datasets to function effectively, the attack surface increases, raising legitimate concerns about unauthorized access or misuse.
Over-reliance on AI presents real risks. If clinicians or patients place excessive trust in algorithms without critically evaluating recommendations, errors may go undetected until they cause harm. There have been documented cases where individuals received harmful AI health recommendations, including one instance where a person following ChatGPT advice about salt water and apple cider vinegar developed acute sodium poisoning.
Lack of transparency complicates accountability. Many AI systems function as “black boxes”—users cannot understand precisely how the system reached its conclusions. This obscures how data is being used and increases privacy risks.
Informed consent challenges arise because patients may not fully understand how their data will be used by AI systems, making genuine informed consent difficult. Additionally, clarity is lacking about data ownership—does patient data belong to the individual, the healthcare provider, the AI company, or all parties?
Moving Forward Responsibly
The integration of AI into personal health management represents a paradigm shift toward proactive, data-driven wellness. The combination of wearable technology, machine learning algorithms, and vast health datasets enables personalization previously impossible.
However, responsible adoption requires balance. AI should enhance human judgment and clinical decision-making, not replace it. Individuals should view AI health tools as valuable supplements to—not substitutes for—relationships with healthcare providers.
Privacy protection is essential. As AI adoption accelerates, strong regulatory frameworks, transparent algorithmic practices, and robust security measures become increasingly important. Individuals should carefully evaluate privacy policies before adopting health apps and maintain awareness of how personal data is being used.
Looking forward, the field must address algorithmic bias, enhance transparency in AI decision-making, establish clearer accountability frameworks, and develop regulations that keep pace with rapid technological change. Collaboration between AI developers, healthcare providers, ethicists, and patient communities is essential to ensure these powerful technologies serve all populations equitably.
When used thoughtfully and critically, AI offers genuine potential to improve health outcomes, increase wellness awareness, and enable earlier intervention in disease processes. The key is approaching these tools with both enthusiasm for their capabilities and vigilance regarding their limitations and ethical implications.